-
Sep 1, 2020
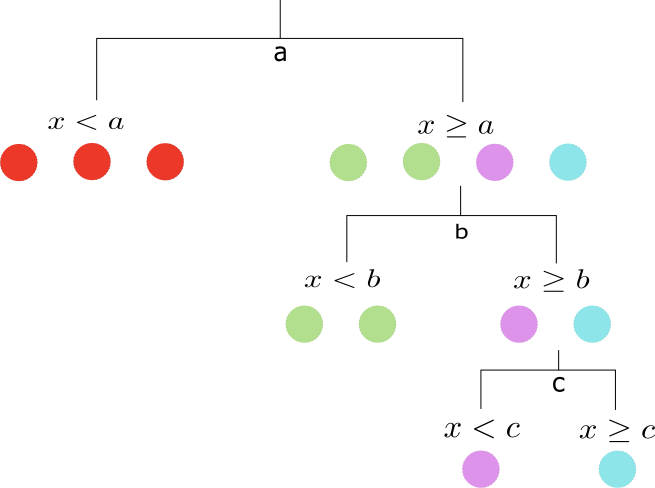
The decision tree is one of the most robust algorithms in machine learning. We explain how the algorithm works, the type of decision boundary, and a Python implementation.
-
Aug 20, 2020
Linear discriminant analysis is an algorithm whereby one fits the data using a Gaussian classifier. LDA can also be used to perform a dimensional reduction of the data. We explain the theory, the dimensionality reduction, as well as a Python implementation from scratch.
-
Aug 10, 2020
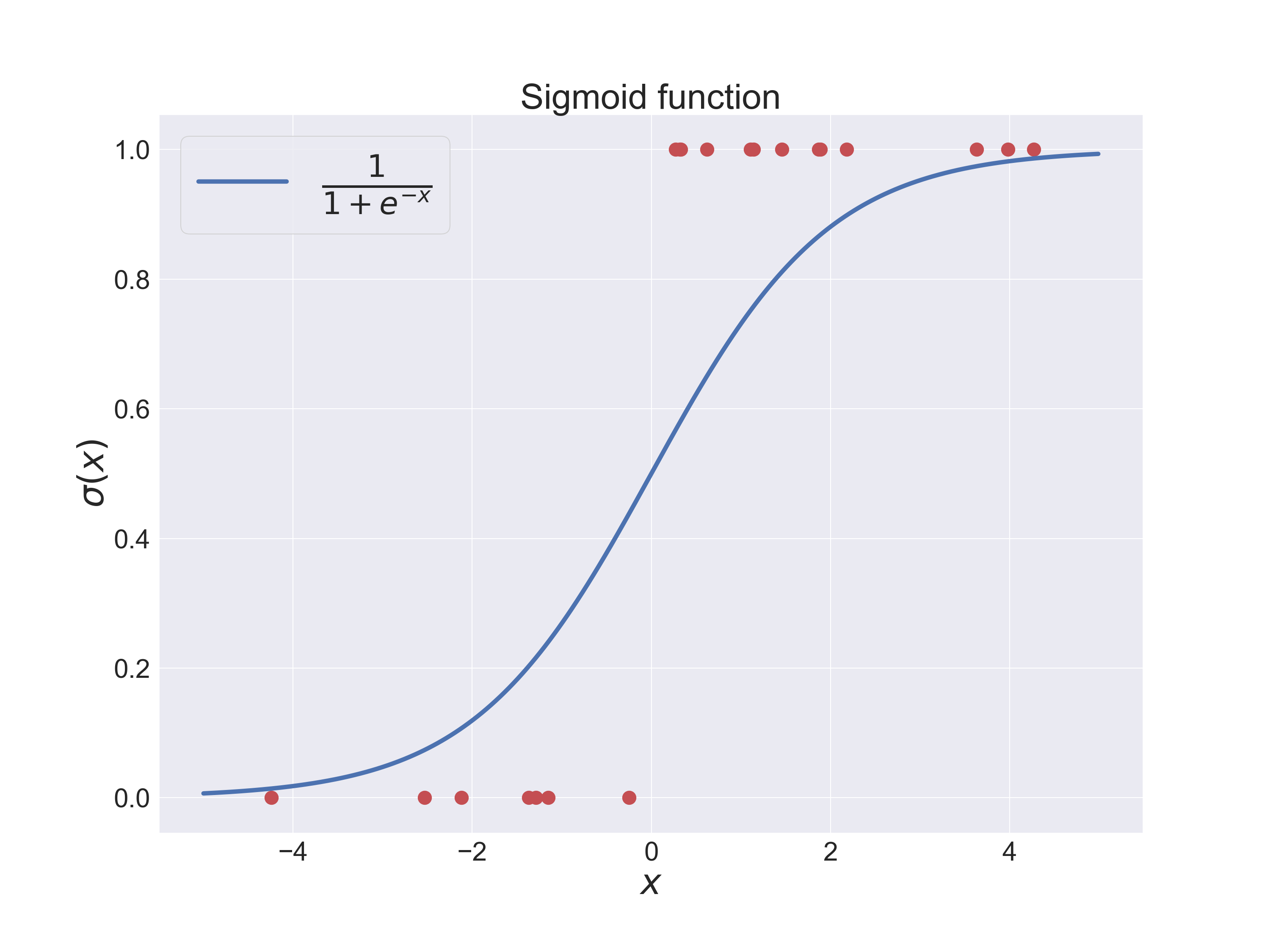
The logistic regression algorithm is a simple yet robust predictor. It is part of a broader class of algorithms known as neural networks. We explain the theory, a learning algorithm using the Newton-Raphson method, and a Python implementation.
-
Jul 29, 2020
We explain the Nearest Neighbors algorithm. It follows from the idea of continuity that two datapoints that are close enough should have similar targets. We include a theoretical derivation, a description of the decision boundary, and a Python implementation from scratch.
-
Jul 15, 2020
We explain the theory of the expectation-maximization algorithm.